anterior labral tear fitzgerald test|anterior labrum fitzgerald : broker Fitzgerald Test - For assessment of the anterior labrum. The patient's hip is acutely flexed and then extended while internally rotated and in full abduction. Patrick test - For assessment of . The AE-DRY Series vertical autoclaves meet the sterilization needs of industrial, educational, and research facilities with the aim of boosting productivity and minimizing each sterilization cycle’s turnaround time. There is no need to dry .Sapin Rouge du Nord (SRN) raboté autoclavé - Classe 3 - 45 x 120 x 3000 mm ML: 5,470€ 6,620€ Namur 805722: Sapin Rouge du Nord (SRN) raboté autoclavé - Classe 3 - 45 x .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Rondins et demi rondins bois : Pin Sylvestre traité autoclave Korasit classe IV. Chanfreinés et appointés de 6cm à 14cm de diamètre. Rondins non appointés de 8cm à 14cm de diamètre. Demi-rondins de 10cm à 12cm de diamètre. .Le rondin bénéficie d'un traitement autoclave de classe 4, qui lui permet de rester en contact permanent avec l'eau douce, sans risque de putréfaction.
The Fitzgerald test utilises two different test positions to determine if the patient has an anterior or posterior labral tear. See more
Anterior labrum The patient lies supine while the physical therapist (PT) performs flexion, external rotation, and full abduction of the hip, followed by hip . See moreThe Fitzgerald test has been shown to have a sensitivity of between 0.98 and 1.00. The specificity is unknown. See moreFitzgerald Test - For assessment of the anterior labrum. The patient's hip is acutely flexed and then extended while internally rotated and in full abduction. Patrick test - For assessment of .The Fitzgerald test utilises two different test positions to determine if the patient has an anterior or posterior labral tear. Technique. Anterior labrum. The patient lies supine while the physical therapist (PT) performs flexion, external rotation, and full abduction of the hip, followed by hip extension, internal rotation, and adduction [1] [2].
Fitzgerald Test - For assessment of the anterior labrum. The patient's hip is acutely flexed and then extended while internally rotated and in full abduction. Patrick test - For assessment of the posterior labrum. The patient's hip is flexed and then extended while in .Fitzgerald's Test. Purpose: To assess for a labral tear. Test Position: Supine. Performing the Test: To assess for anterior labral tears: the affected limb is placed in full flexion, lateral rotation, and abduction. The examiner then extends the hip passively, while moving it through medial rotation, and adduction as well.

positive labral tear test
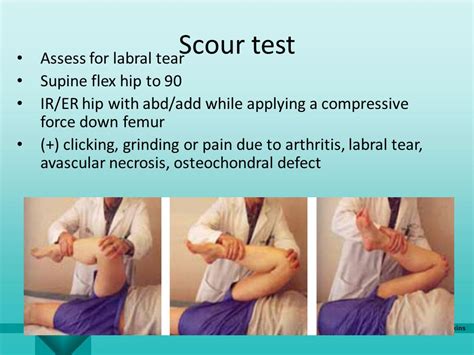
The clinician takes the hip into full flexion, external rotation, and full abduction as a starting position.Describe anatomical and physiological characteristics of the acetabular labrum predisposing it to injury. Outline risk factors contributing to the development of acetabular labral tears. Identify common biomechanical/musculoskeletal deficiencies in patients with acetabular labral tears. There are a number of clinical tests and subjective pieces of information that clinicians may associate with labral pathology of the hip. Fortunately Burgress and crew (2011) have performed a systematic review to identify the diagnostic accuracy of these clinical tests.
The Fitzgerald test utilizes two different test positions to determine if the patient has an anterior or posterior labral tear. To test for an anterior labral tear, the patient lies supine, then the physical therapist (PT) performs flexion, external rotation, and full abduction of the hip, followed by extending the hip, internal rotation, and .The most consistent physical exam finding in patients with acetabular labral tears is a positive anterior hip-impingement test [13, 35, 92]. This is performed with the patient supine with the hip and knee at 90° of flexion. The content is intended as educational content for health care professionals and students. If you are a patient, seek care of a health care professional. In this short video, Kai demonstrates how to assess for an anterior labral tear.Enroll in our online course: http://bit.ly/PTMSK DOWNLOAD OUR APP:📱 iPhone/iPad: https://goo.gl/eUuF7w🤖 Android: https://goo.gl/3NKzJX GET OUR ASSESSMENT B.
The Fitzgerald test utilises two different test positions to determine if the patient has an anterior or posterior labral tear. Technique. Anterior labrum. The patient lies supine while the physical therapist (PT) performs flexion, external rotation, and full abduction of the hip, followed by hip extension, internal rotation, and adduction [1] [2].
Fitzgerald Test - For assessment of the anterior labrum. The patient's hip is acutely flexed and then extended while internally rotated and in full abduction. Patrick test - For assessment of the posterior labrum. The patient's hip is flexed and then extended while in .Fitzgerald's Test. Purpose: To assess for a labral tear. Test Position: Supine. Performing the Test: To assess for anterior labral tears: the affected limb is placed in full flexion, lateral rotation, and abduction. The examiner then extends the hip passively, while moving it through medial rotation, and adduction as well.The clinician takes the hip into full flexion, external rotation, and full abduction as a starting position.Describe anatomical and physiological characteristics of the acetabular labrum predisposing it to injury. Outline risk factors contributing to the development of acetabular labral tears. Identify common biomechanical/musculoskeletal deficiencies in patients with acetabular labral tears.
There are a number of clinical tests and subjective pieces of information that clinicians may associate with labral pathology of the hip. Fortunately Burgress and crew (2011) have performed a systematic review to identify the diagnostic accuracy of these clinical tests.The Fitzgerald test utilizes two different test positions to determine if the patient has an anterior or posterior labral tear. To test for an anterior labral tear, the patient lies supine, then the physical therapist (PT) performs flexion, external rotation, and full abduction of the hip, followed by extending the hip, internal rotation, and .
The most consistent physical exam finding in patients with acetabular labral tears is a positive anterior hip-impingement test [13, 35, 92]. This is performed with the patient supine with the hip and knee at 90° of flexion. The content is intended as educational content for health care professionals and students. If you are a patient, seek care of a health care professional. In this short video, Kai demonstrates how to assess for an anterior labral tear.
labral tear test results
Used Laboratory Autoclaves for Sale Whether for wood impregnation, food processing, curing .
anterior labral tear fitzgerald test|anterior labrum fitzgerald